Showing 1–12 of 24 results
-
- Low Melting Point: Excellent for low-temperature soldering and thermal interface materials.
- Thermoelectric Properties: Exhibits promising performance in energy harvesting systems.
- Customizable Particle Size: Available in various sizes tailored to application needs.
- High Purity: Ensures reliable performance in precision applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: Contains no lead, making it suitable for eco-friendly applications.
-
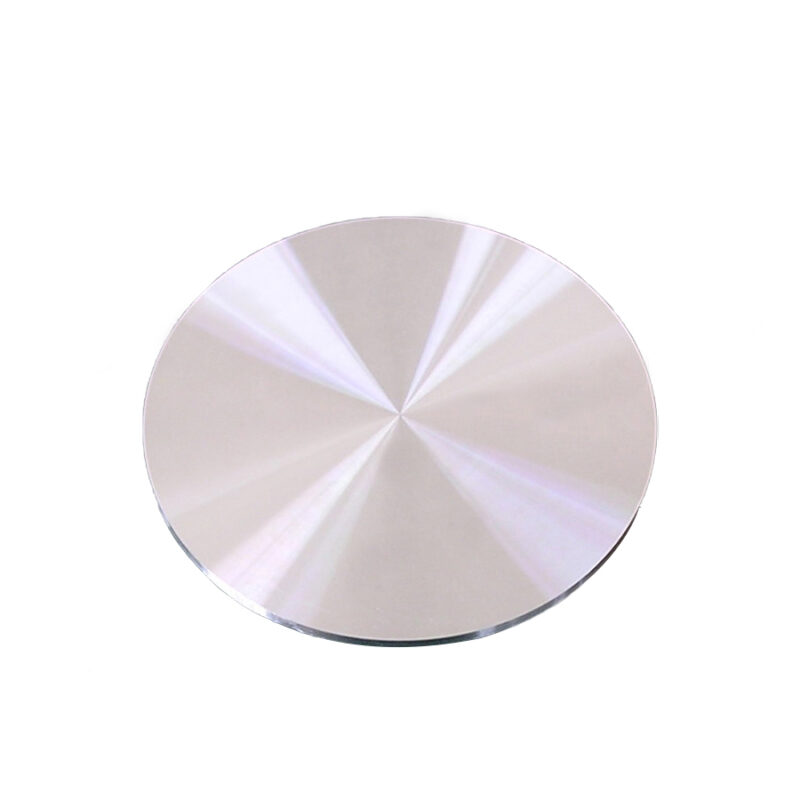

- High Solar Absorption Efficiency: CuIn alloy thin films exhibit excellent light absorption properties, contributing to the high efficiency of CIGS solar cells in converting solar energy into electricity.
- Bandgap Tunability: CuIn alloys enable tuning of the material’s bandgap to optimize its performance for specific photovoltaic applications.
- Lightweight and Flexible: CuIn-based thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for both rigid and flexible solar panel designs.
- Thermal and Chemical Stability: The CuIn alloy demonstrates good thermal and chemical stability, ensuring durability in outdoor and harsh environmental conditions, which is essential for long-lasting solar cells.
- Customizable Composition: The ratio of copper to indium in the alloy can be adjusted to meet specific application requirements, ensuring tailored properties for different solar and electronic devices.
-
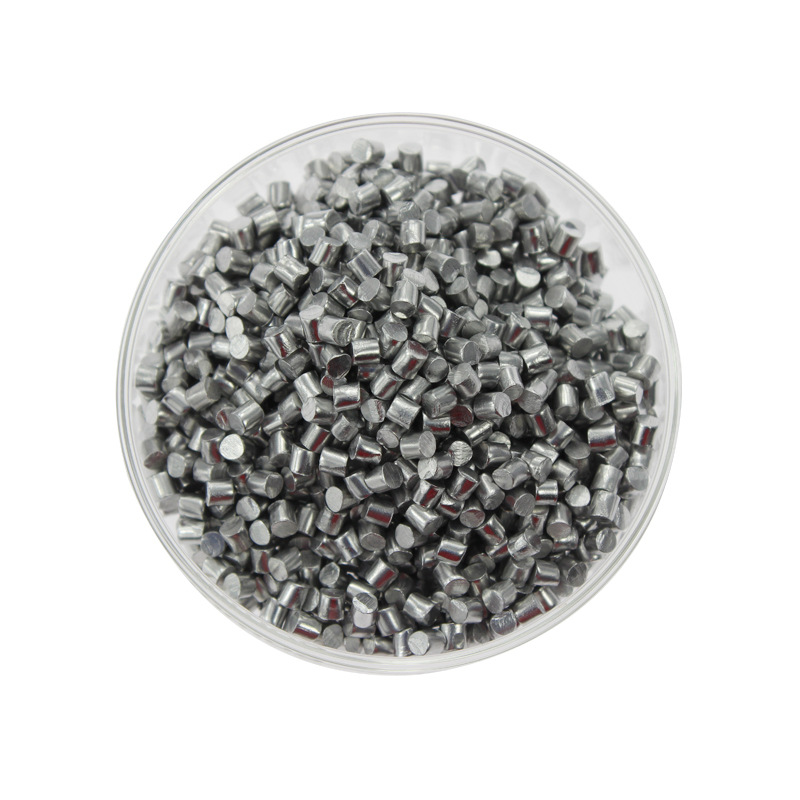

- High Conductivity: Excellent electrical properties ideal for semiconductor applications.
- Thermal Stability: Maintains performance in high-temperature environments.
- Compatibility: Works well with various deposition techniques, including thermal evaporation and sputtering.
- Customizable Composition: Can be tailored with different copper to indium ratios to meet specific application needs.
-
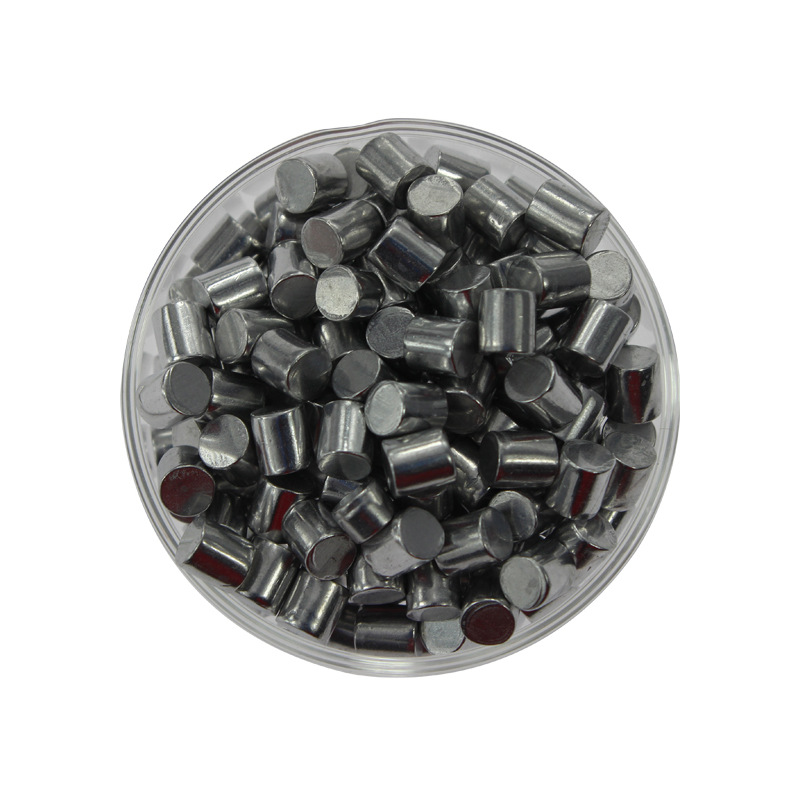

- High Efficiency: Offers excellent conversion efficiency in solar cells, making it a preferred choice in renewable energy applications.
- Versatile Composition: The ability to adjust the ratio of copper, indium, and gallium allows for customization of electronic properties.
- Good Thermal Stability: Maintains performance over a wide temperature range.
-
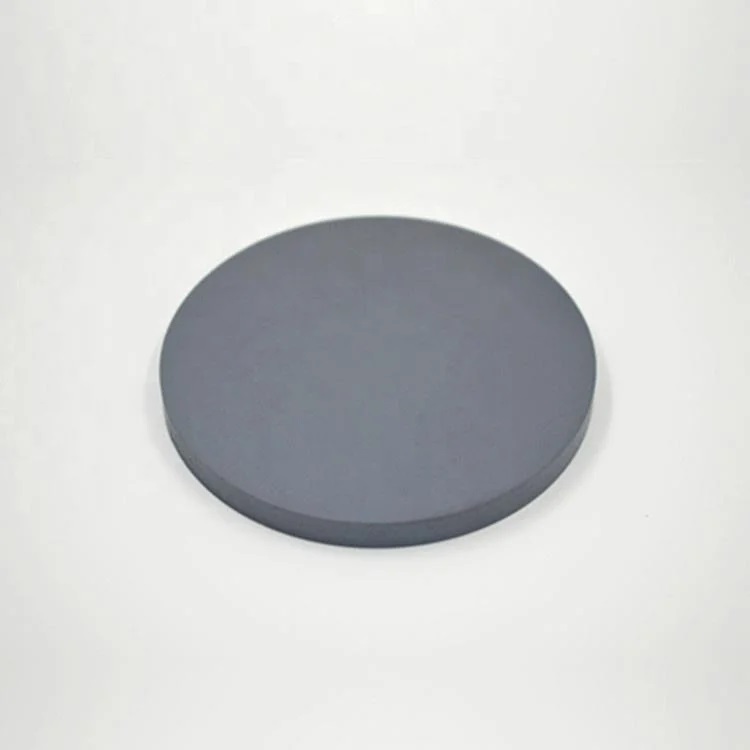
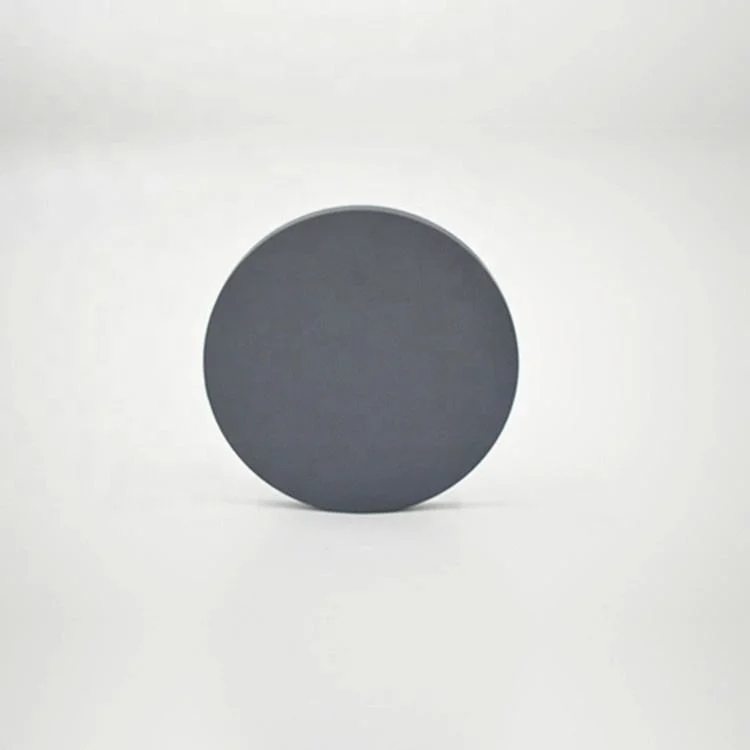


- High Solar Conversion Efficiency: CuInGaSe (CIGS) thin films exhibit high energy conversion efficiency, particularly in thin-film photovoltaic cells, making them an ideal choice for modern solar technology.
- Wide Bandgap Tunability: The presence of gallium allows for tuning the bandgap, which improves the absorption spectrum and efficiency of solar cells.
- Lightweight and Flexible: CIGS thin-film solar panels are lighter and more flexible compared to traditional silicon-based panels, enabling their use in various applications, from portable devices to large-scale installations.
- Excellent Absorption Properties: CIGS thin films offer superior absorption of sunlight across a wide range of wavelengths, making them more effective at capturing solar energy, even in diffuse or low-light conditions.
- Stable in Harsh Conditions: CuInGaSe thin films provide stability and performance reliability in a range of environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance in solar panels.
-
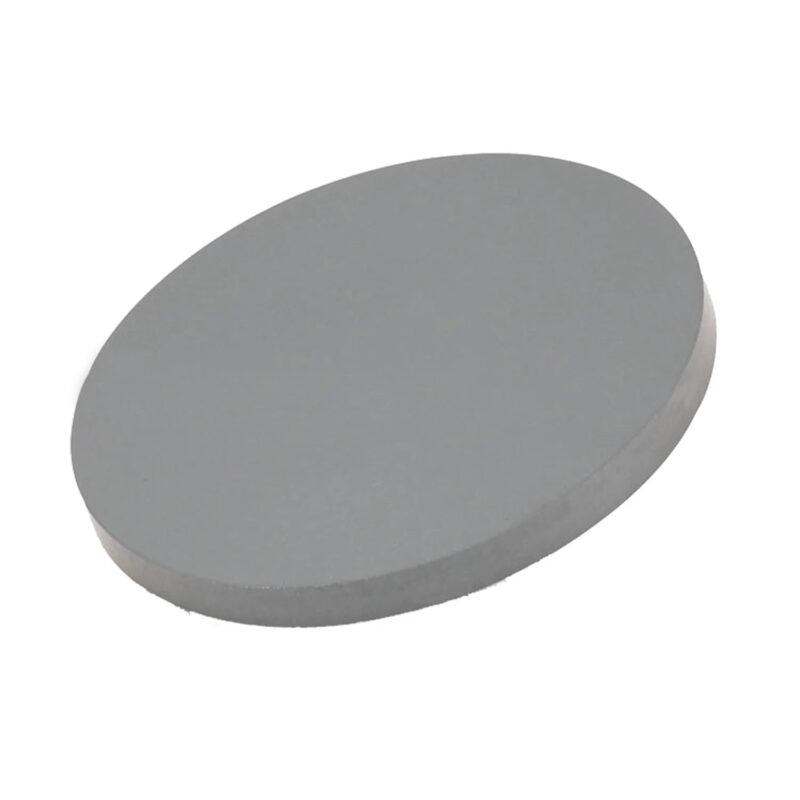
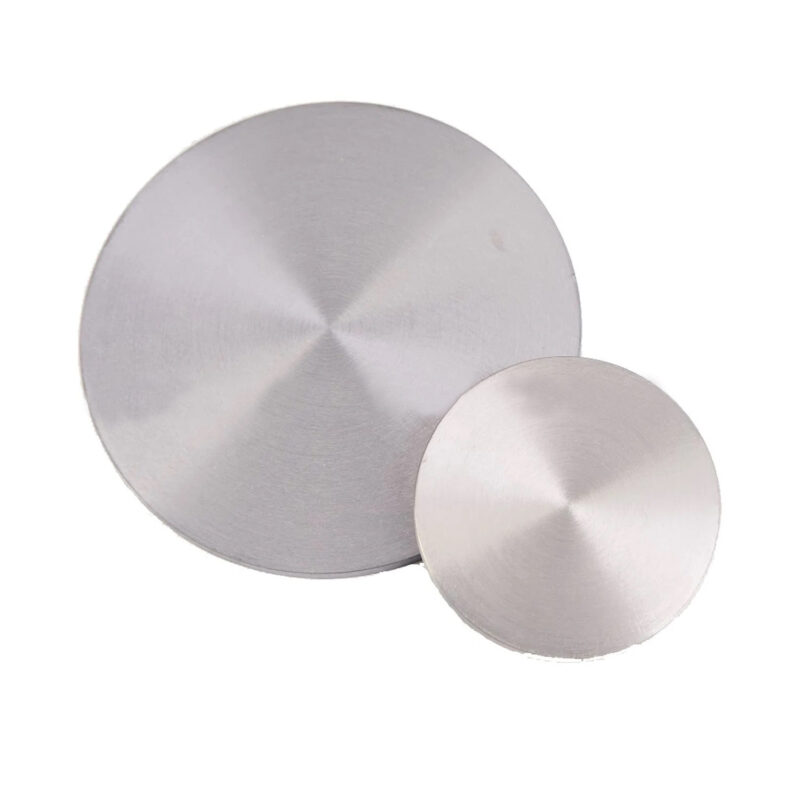


- High Electron Mobility: IGZO offers much higher electron mobility than amorphous silicon, leading to faster switching speeds and improved performance in TFT-based devices.
- Low Power Consumption: IGZO thin films help reduce power usage in displays and electronics, making them ideal for energy-efficient applications.
- Transparency: IGZO is a transparent conductive oxide, which is essential for applications in display and touch panel technologies.
- Thermal Stability: IGZO provides excellent thermal stability, ensuring reliable performance even under high temperatures during processing.
- Scalability for High-Resolution Displays: Due to its high electron mobility, IGZO is well-suited for producing ultra-high-resolution displays (such as 4K and 8K) with faster refresh rates and greater detail.
-
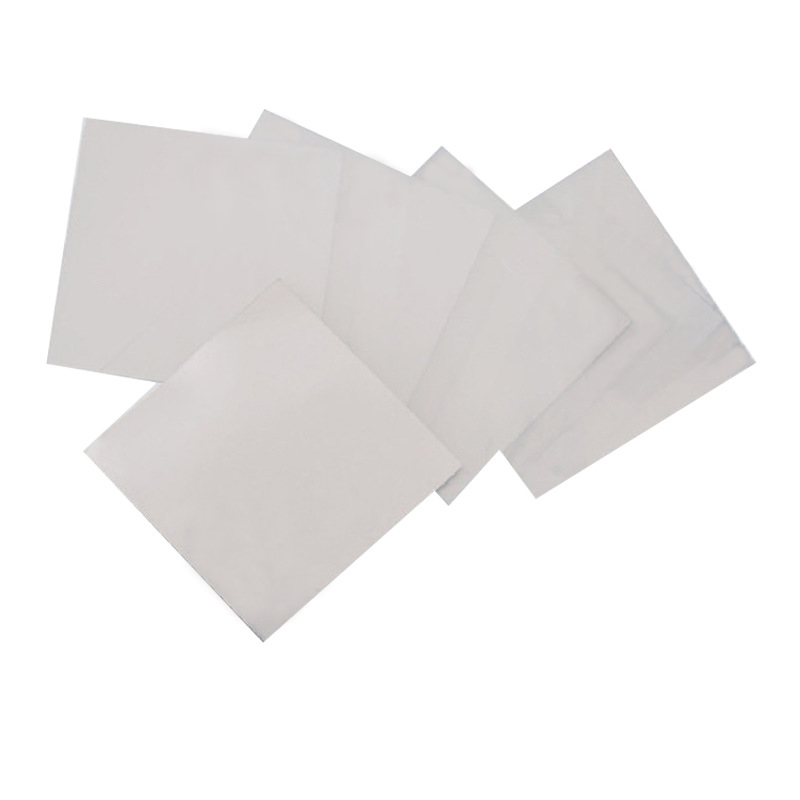


- High Ductility and Malleability: Indium foil is exceptionally soft and pliable, allowing it to conform to complex shapes without cracking or losing its integrity.
- Thermal Conductivity: Indium foil efficiently transfers heat, making it an excellent thermal interface material (TIM) in electronics and other high-precision applications.
- Electrical Conductivity: With its excellent electrical conductivity, indium foil is often used in electrical and electronic devices.
- Corrosion Resistance: Indium has good resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it reliable for long-term use in harsh environments.
- Low Melting Point: Indium has a relatively low melting point of 156.6°C, which allows it to be used in specialized low-temperature soldering applications.
- Non-Toxic and Biocompatible: Indium foil is non-toxic and safe for use in medical and scientific applications.
-

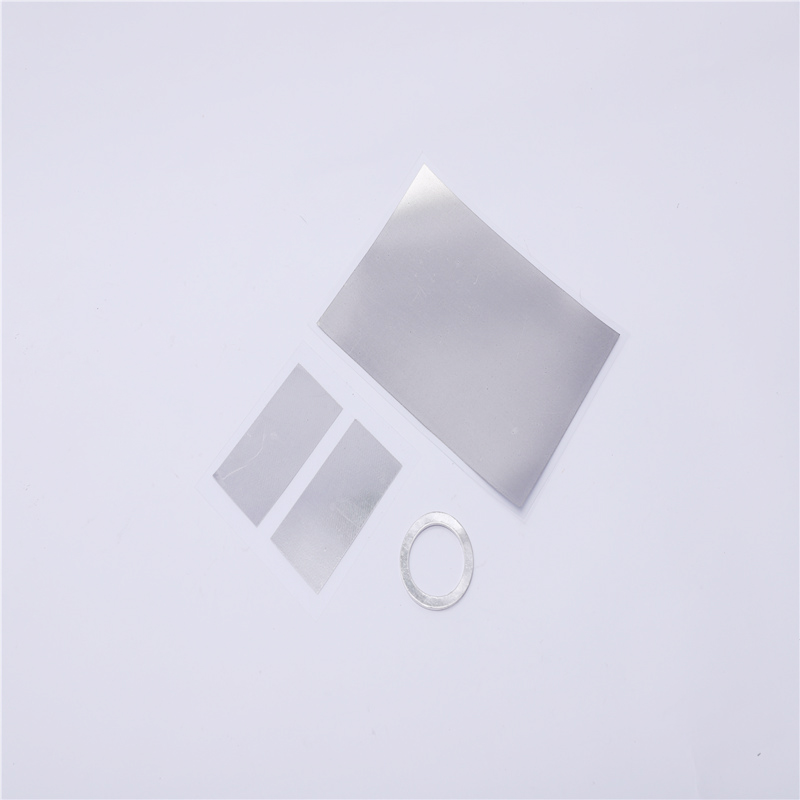
- Low Melting Point: Indium has a melting point of 156.6°C, making it suitable for soldering and low-temperature applications.
- High Conductivity: Indium films provide good electrical and thermal conductivity, ideal for electronic and thermal management applications.
- Excellent Wetting Properties: Indium forms strong bonds with glass, metals, and ceramics, ensuring effective adhesion in coatings and soldering applications.
- Ductile and Malleable: Indium is highly ductile, allowing for easy deposition and shaping into thin films or intricate structures.
- Corrosion Resistant: Indium is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, ensuring long-lasting durability in various environments.
-

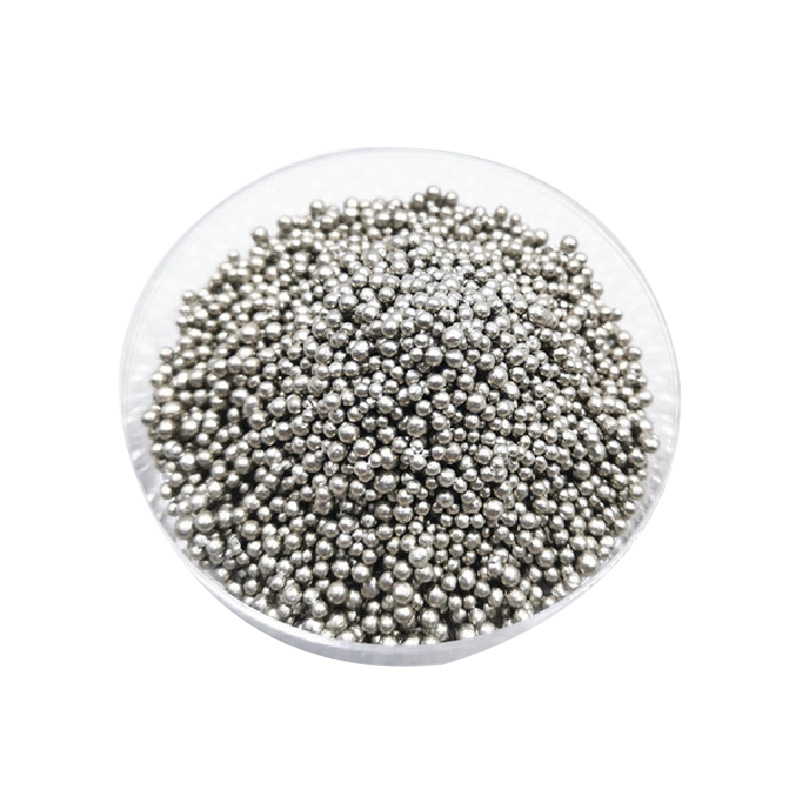
- High Purity: Ensures reliable performance in sensitive electronic and industrial applications.
- Low Melting Point: Ideal for soldering and thermal interface materials.
- Excellent Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Facilitates efficient energy transfer.
- Soft and Malleable: Easily forms thin films and intricate shapes.
- Corrosion Resistance: Stable in various environmental conditions.
-


- High Purity: Available in high-purity grades to ensure excellent film quality and performance.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Indium offers great conductivity, making it ideal for electronic and optical applications.
- Malleability: The material can be easily shaped and deposited to meet specific needs.
- Uniform Deposition: Ensures high-quality and uniform films, critical for advanced technologies.
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to corrosion, enhancing the durability and longevity of the coatings.
-

- Excellent Electrical Conductivity: Indium wire is highly conductive, making it essential in electrical and electronic applications where efficient current flow is required.
- Low Melting Point: With a melting point of 156.6°C, indium wire is ideal for low-temperature applications, especially in the soldering and bonding processes.
- High Malleability and Ductility: Indium is soft and easily formable, which allows for precise shaping and manipulation in various applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: It is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, ensuring longevity and reliability even in harsh environments.
- Non-toxic and Biocompatible: Indium is considered non-toxic and biocompatible, making it safe for use in medical and electronic devices.
- Thermal Conductivity: While not as high as metals like copper, indium’s thermal conductivity is suitable for applications requiring moderate heat transfer.
- Customizability: Indium wire is available in different diameters, purities, and finishes, providing flexibility to meet specific needs.
-

- High Electrical Conductivity: In₂O₃ is known for its ability to conduct electricity while maintaining optical transparency, making it ideal for transparent electrodes.
- Optical Transparency: Provides high transparency in the visible and near-infrared regions, ensuring excellent optical clarity in thin films.
- High Purity: Available in ≥ 99.9% purity, ensuring high-quality deposition for sensitive applications.
- Stable Film Deposition: Exhibits excellent thermal stability, allowing for uniform and stable film formation during evaporation processes.
- Versatility: Can be used in a variety of deposition techniques, including e-beam evaporation and thermal evaporation.
















