Showing 217–228 of 632 results
-

- High Purity: Available in 99.99% (4N) or higher purity levels to ensure contamination-free thin films, crucial for high-precision semiconductor and optoelectronic applications.
- Low Melting Point: Gallium’s low melting point (29.76°C) allows for easy evaporation and controlled deposition processes.
- Good Wetting Properties: Gallium forms uniform films with excellent adhesion to substrates, critical for consistent and reliable thin-film layers.
- Optoelectronic Properties: Gallium’s ability to form gallium-based compounds, such as GaAs and GaN, makes it indispensable in high-performance optoelectronics.
- Versatile Deposition: Suitable for use in thermal and electron beam evaporation systems for consistent and high-quality film growth.
- Chemical Stability: Gallium is resistant to oxidation, ensuring stable and long-lasting films in various environments.
-

- Wide Bandgap (4.8 eV): Ga₂O₃ is a wide-bandgap semiconductor, offering superior electrical performance in power electronics and UV detection.
- High Optical Transparency: Ga₂O₃ is transparent in the UV-visible range, making it an ideal material for optical applications.
- High Thermal and Chemical Stability: The material exhibits stability under extreme thermal conditions, enhancing its performance in harsh environments.
- Excellent Thin Film Quality: Ga₂O₃ forms smooth, uniform thin films, ensuring high precision in electronic and optical devices.
- Low Cost and Availability: Compared to other wide-bandgap semiconductors like SiC or GaN, Ga₂O₃ offers a cost-effective alternative for high-performance electronics.
-

- Wide Bandgap: Enables applications in high-power and high-frequency electronic devices.
- High Purity: Ensures reliability and performance in critical applications.
- Thermal Stability: Excellent performance in high-temperature environments.
- UV Transparency: Outstanding optical properties for UV applications.
- Customizable Particle Size: Tailored to meet specific application requirements.
-
- Chemical Formula: GaN
- Molecular Weight: 83.73 g/mol
- Density: 6.15 g/cm³
- Bandgap: ~3.4 eV
- Melting Point: ~2500°C (decomposes)
- Purity Levels: 99.99% (4N), 99.999% (5N)
- Electrical Conductivity: High electron mobility and breakdown voltage
- Thermal Conductivity: Excellent heat dissipation for high-power applications
-
- Wide Bandgap: GaS possesses a wide bandgap of about 2.5 eV, making it suitable for UV and visible light applications.
- High Purity: GaS targets are available in high-purity forms to ensure the quality and performance of the deposited films.
- Layered Structure: The layered nature of GaS allows for easy mechanical exfoliation, enabling the production of high-quality monolayers and thin films.
- Thermal Stability: GaS exhibits good thermal stability, maintaining its properties during high-temperature processing.
- Good Electrical Conductivity: GaS is a good electrical conductor, making it valuable in electronic applications.
-
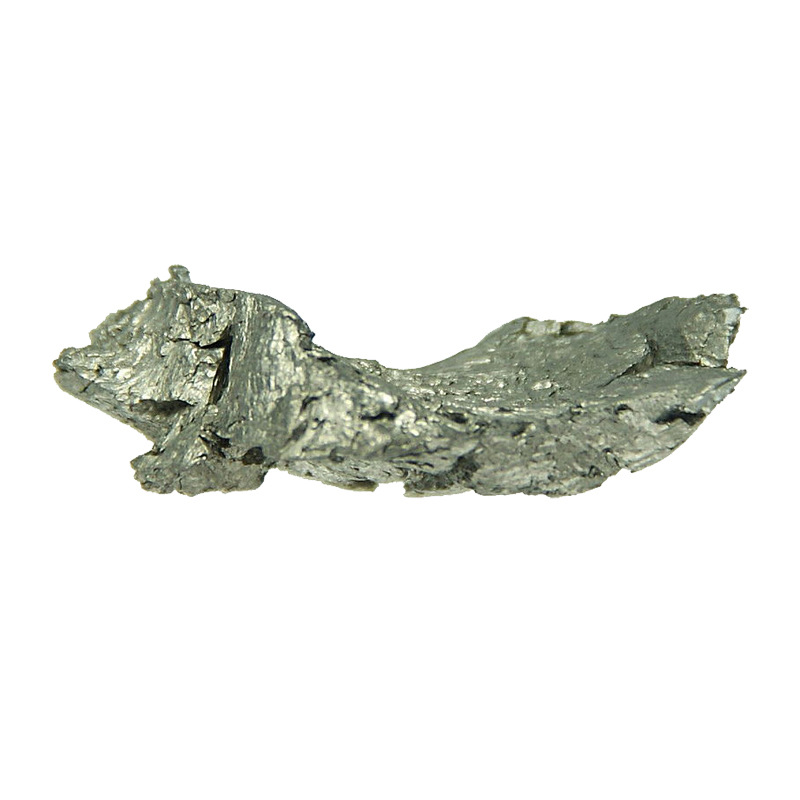

- Strong Magnetic Properties: Gadolinium exhibits significant paramagnetic behavior, especially near room temperature, making it useful in advanced magnetic applications.
- Optical and Thermal Stability: Gadolinium’s stability at high temperatures allows it to be deposited as a durable thin film in various optical and thermal applications.
- High Purity: The high purity of Gadolinium ensures optimal performance in precision deposition processes like thermal evaporation and e-beam evaporation.
- Rare-Earth Luminescence: Gadolinium can be used in luminescent materials, enhancing performance in lighting and display technologies.
-
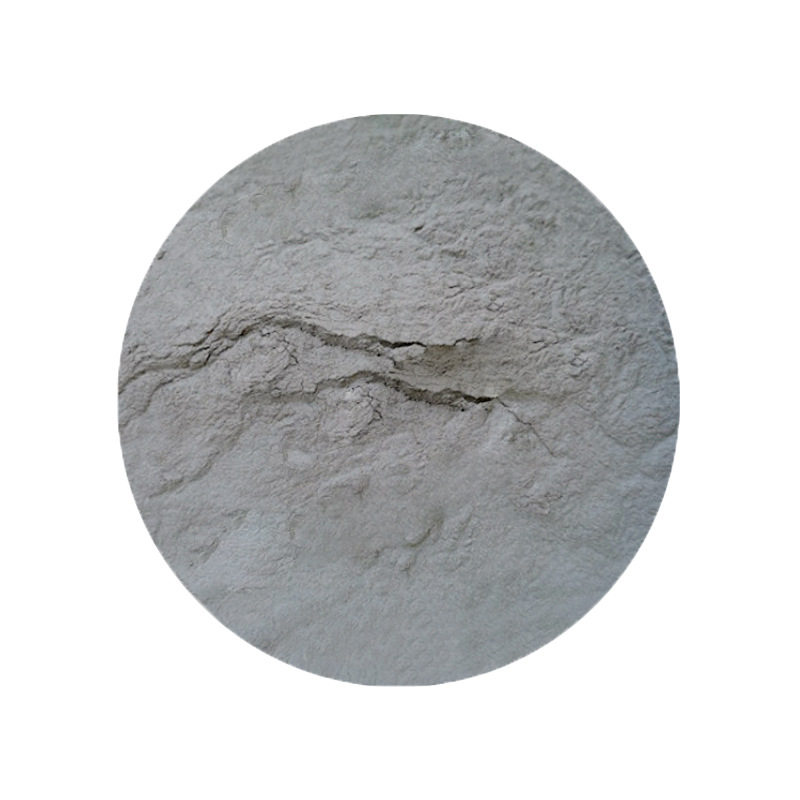

- Magnetocaloric Properties: Gadolinium exhibits a large magnetocaloric effect, making it highly valuable in solid-state refrigeration systems.
- Neutron Absorption: Gadolinium is one of the best materials for absorbing neutrons, making it indispensable for nuclear reactors and radiation shielding.
- Magnetic Properties: Gadolinium is strongly magnetic at low temperatures (below 20°C), with a Curie temperature of around 293 K (20°C), where it loses its ferromagnetic properties.
- Thermal Stability: Gadolinium powder has excellent thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for use in nuclear and high-temperature applications.
- Chemical Reactivity: Gadolinium is relatively stable in dry air but reacts with moisture, forming gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) on the surface.
-
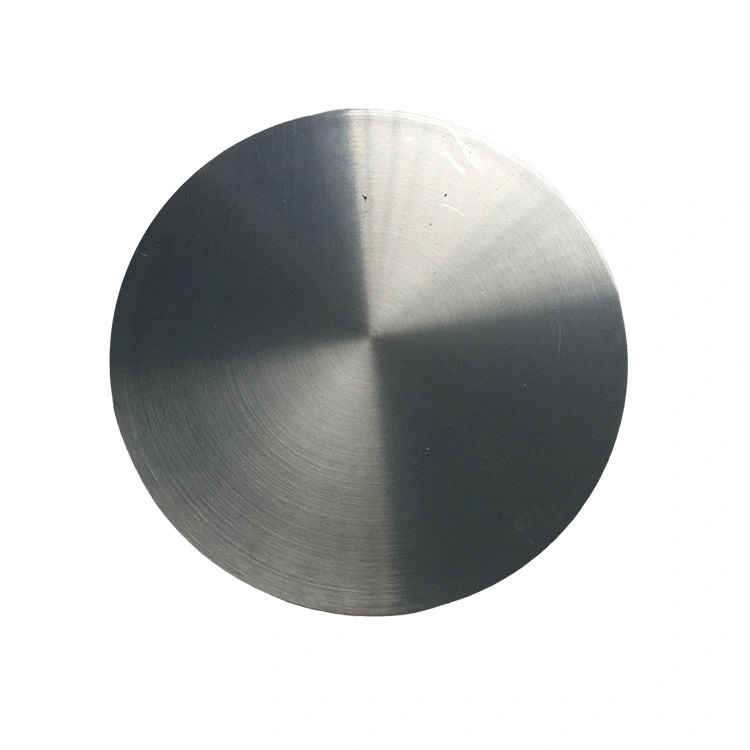

- Purity: Typically available at 99.9% or higher purity to ensure optimal film quality and performance.
- Customizable Size and Shape: Gadolinium sputtering targets are available in various forms, such as discs, plates, or cylinders, tailored to specific deposition systems.
- Magnetic Properties: Gadolinium’s strong magnetic characteristics are highly desirable in magnetic thin films.
- Oxidation Resistance: Gadolinium can be coated or alloyed to prevent oxidation during sputtering.
-
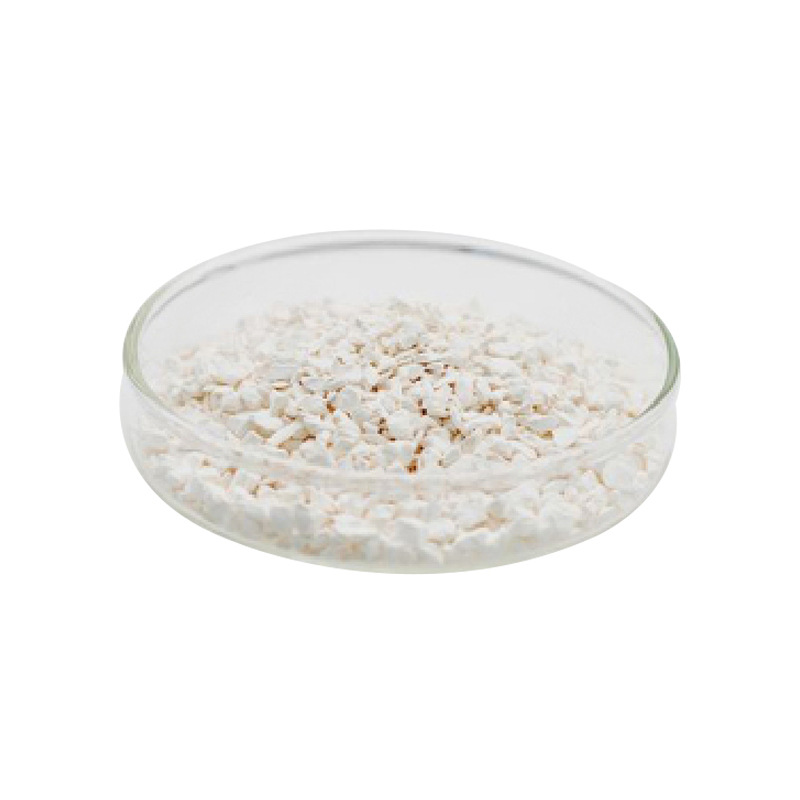

- Magnetic Properties: Exhibits strong paramagnetism, making it useful in magneto-optical and spintronic devices.
- High Dielectric Constant: Gd₂O₃ has a high dielectric constant, making it an excellent material for electronics and capacitors.
- Thermal Stability: Gd₂O₃ can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
- Optical Transparency: It has excellent transparency in both visible and infrared wavelengths, ideal for optical coatings.
- Chemical Inertness: Highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, ensuring long-term stability of thin films.
-

- High Purity: Ensures optimal performance in sensitive applications.
- Magnetic Properties: Ideal for magnetic refrigeration and data storage applications.
- High Refractive Index: Suitable for advanced optical components.
- Thermal Stability: Performs reliably in high-temperature environments.
- Customizable Particle Size: Adaptable for various industrial and research needs.
-


- High Purity: Available in high-purity levels to ensure the quality of thin films for sensitive electronic and optical applications.
- Magnetic Properties: Gd₂O₃ exhibits strong magnetic behavior, making it suitable for applications in magnetic storage and spintronic devices.
- High-k Dielectric: Its high dielectric constant makes Gd₂O₃ ideal for use in semiconductor devices as a gate dielectric material.
- Thermal Stability: Gd₂O₃ is thermally stable, maintaining its structural integrity and properties during high-temperature processes.
-

- High Refractive Index: Germanium has a high refractive index (around 4.0 at 10 µm), making it ideal for IR optics and imaging systems.
- Broad Infrared Transparency: Germanium is transparent in the infrared spectrum, making it suitable for IR optical coatings, lenses, and filters.
- Excellent Electron Mobility: Germanium’s electron mobility is higher than silicon, enhancing its application in semiconductor devices.
- High Purity: Germanium used in evaporation is highly purified (typically ≥ 99.99%), ensuring uniform and high-quality thin films.
- Low Melting Point: Germanium has a relatively low melting point (937°C), making it easy to evaporate in standard PVD systems.
- Compatible with Silicon: Germanium is often used in conjunction with silicon in semiconductor and optoelectronic applications.














